Slitting and rewinding machine is a key equipment in packaging, printing, film and other industries, and its operation stability directly affects production efficiency and product quality. The following is a systematic summary of common fault diagnosis and solutions for engineers' reference:
First, material-related failures
1. Wrinkles/creases on the surface of the coil
◦ Causes: uneven tension, deviation of the parallelism of the guide rollers, insufficient air pressure (air shaft), uneven thickness of the material itself.
◦ Solution:
▪ Check and adjust the unwinding/rewinding tension gradient (increasing or decreasing step by step).
▪ Calibrate the parallelism of the guide rollers with a spirit level (error ≤ 0.05mm/m).
▪ Clean or replace the air expansion shaft airbag to ensure that the air pressure ≥ 0.6MPa.
2. Fracture of the edge of the material
◦ Causes: passivation of the slitting knife, deviation of the angle of the tool holder, brittleness of the material (such as BOPP film).
◦ Solution:
▪ Replace the round blade (it is recommended to check the sharpness of the knife edge every shift).
▪ Adjust the blade tilt angle (usually between 15°-25°).
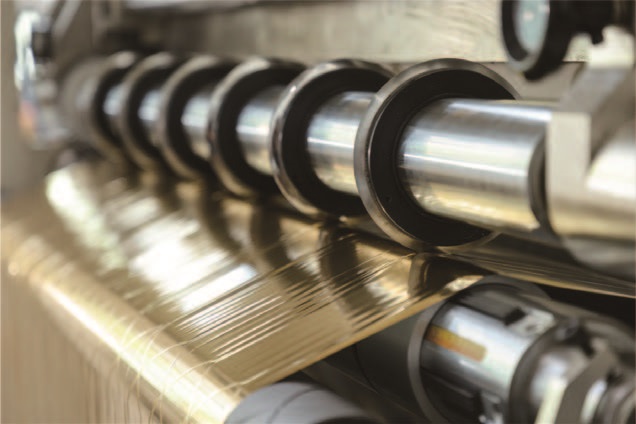

Second, mechanical transmission failure
1. Uneven winding (chrysanthemum pattern)
◦ Causes: core eccentricity, uneven pressure of the pressure roller, EPC deviation correction failure.
◦ Solution:
▪ Use a dial gauge to detect core radial runout (standard ≤ 0.02mm).
▪ Calibrate the linear pressure of the roller (tested by a pressure distribution meter).
▪ Clean the EPC photoelectric sensor and check the cylinder response speed (normal ≤0.1s).
2. Abnormal vibration of the device
◦ Causes: Bearing wear (especially slitting shaft bearings), balance failure, loose foundation.
◦ Solution:
▪ Use the listening stick to determine the position of the abnormal noise, and replace high-precision bearings such as SKF/NSK.
▪ Dynamic balance correction for high-speed rollers (>800m/min) (G2.5 standard).
Third, electrical control system failure
1. The tension fluctuates greatly
◦ Causes: Encoder signal interference, PLC PID parameter drift, brake slippage.
◦ Solution:
▪ A magnetic ring filter is installed, and the encoder wire is changed to a twisted-pair shielded wire.
▪ Retune the PID parameters (proportional band recommended initial value of 40%-60%).
▪ Check the magnetic particle brake clearance (standard 0.3-0.5mm) and replace the expired magnetic particle.
2. The human-machine interface (HMI) is unresponsive
◦ Cause: communication module failure, power supply voltage fluctuation, program jamming.
◦ Solution:
▪ Restart the PLC (pay attention to the backup parameters) and check the stability of the 24V power supply (fluctuation ± less than 5%).
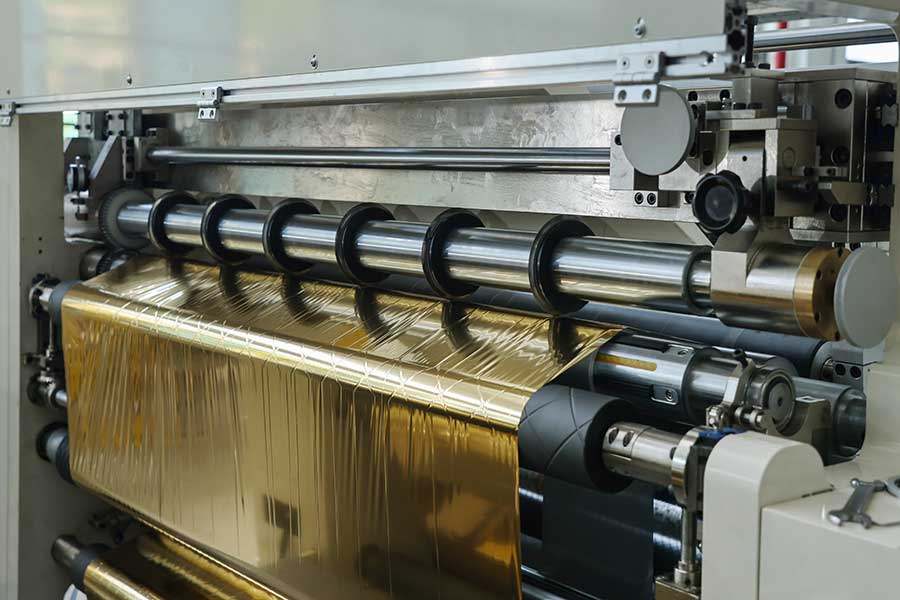

Fourth, the tool system failure
1. Slitting burrs/dust
◦ Causes: Mismatch of blade material (e.g., tungsten steel knife is required for cutting PET), improper overlap of upper and lower knives.
◦ Solution:
▪ Choose the tool according to the hardness of the material (refer to the Mohs scale).
▪ Adjust the amount of overlap (typically 10%-20% of the thickness of the material).
2. Automatic sharpening fails
◦ Causes: Worn grinding wheels, overloaded feed servos.
◦ Solution:
▪ Replace the CBN grinding wheel (120-180 grit size recommended).
▪ Check the servo motor current (within ±15% of the rated value).
Fifth, hydraulic/pneumatic failure
1. The pressure roller is stuck in the lifting and stagnation
◦ Causes: aging of cylinder seals, blockage of solenoid valves, and insufficient lubrication of guide rails.
◦ Solution:
▪ Use a high-temperature sealing ring (e.g. fluoroelastomer).
▪ Clean the SMC/FESTO solenoid valve and confirm the oil supply to the lubricator (3-5 drops/min).
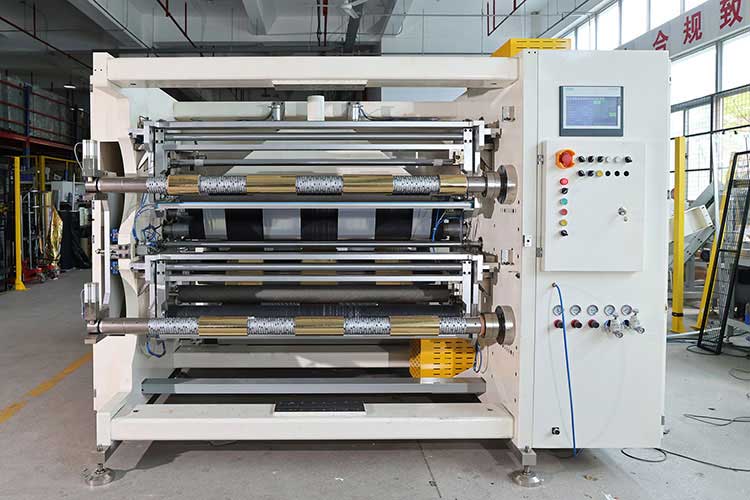

Sixth, preventive maintenance recommendations
1. Daily spot check: check the barometer, tension display value, and tool status.
2. Monthly maintenance: lubricate the linear guide (using ISO VG68 lubricating oil) and calibrate the sensor.
3. Annual overhaul: change of gear gear oil (Mobilgear 600XP recommended), full calibration of the control system.
Typical case: The winding serpentine misalignment problem of a PE film production line was finally found to be due to the stain on the EPC correction mirror, which caused the photoelectric signal to attenuate (the misalignment was reduced from ±5mm to ±1mm after cleaning).
Through systematic diagnosis and precise maintenance, the failure rate of the slitter rewinder can be significantly reduced (empirical data: downtime is reduced by more than 60%). It is recommended to establish a device health file and record the historical curves of key parameters for trend analysis.

This is not only an iteration of equipment, but also a comprehensive redefinition of production efficiency, material utilization and intelligent management standards.
27. February, 2026
It is in this context that the new generation of ribbon slitting machines is redefining the production standards of the industry with "precision manufacturing" as the core.
27. February, 2026
this once management pain point is now transforming into a powerful tool for printing enterprises to reduce costs and increase efficiency.
26. February, 2026
This article will delve into how to make the hot foil slitting machine the engine of your production process optimization through scientific equipment selection and management.
26. February, 2026
A precision platform that integrates multifunctional applications with cross-disciplinary process expansion.
26. February, 2026