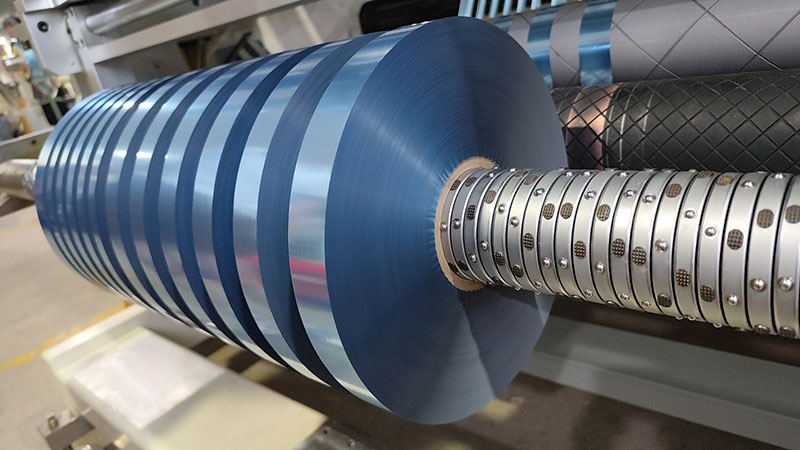
The high-precision cutting function of the slitter significantly improves product quality while optimizing production efficiency and cost control by:
1. Dimensional accuracy and consistency
• Tight tolerance control: The high-precision slitting machine can achieve a cutting tolerance of ±0.1mm or even lower, ensuring that the size of each piece of material fully meets the design requirements, and avoiding assembly problems or appearance defects caused by dimensional deviations.
• Batch consistency: Through servo system or laser positioning technology, the dimensional uniformity of each slitting unit is guaranteed during high-volume production, reducing batch variation.
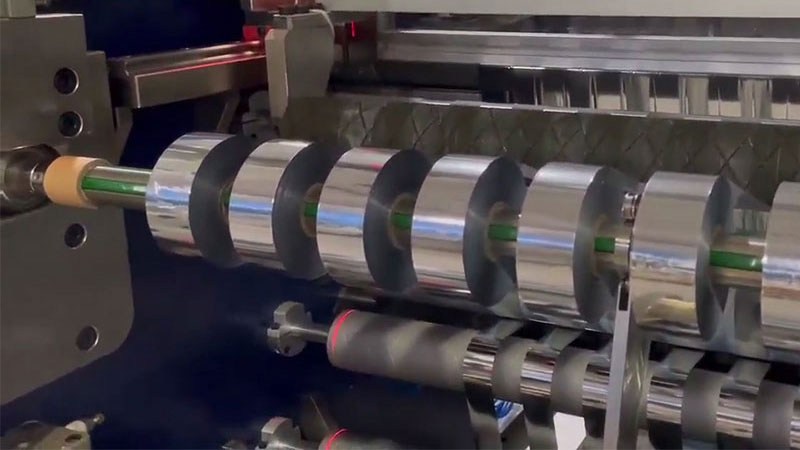

2. Edge quality optimization
• Reduced burrs and delamination: Smooth edges with hard tools (e.g. diamond coating) or laser cutting technology are essential for delicate materials such as films and composites.
• Reduce the need for subsequent processing: High-quality cutting can directly reduce secondary processes such as grinding and trimming, and shorten the production cycle.
3. Material utilization rate is improved
• Intelligent nesting and minimization of waste: Optimize the cutting path through the numerical control system (CNC) to maximize the material utilization rate (such as dynamic adjustment of the slitting width of the coil), and directly reduce the waste of raw materials.
• Reduced slitting loss: High-precision guiding systems (e.g., CCD visual guidance) avoid edge waste caused by material misalignment.
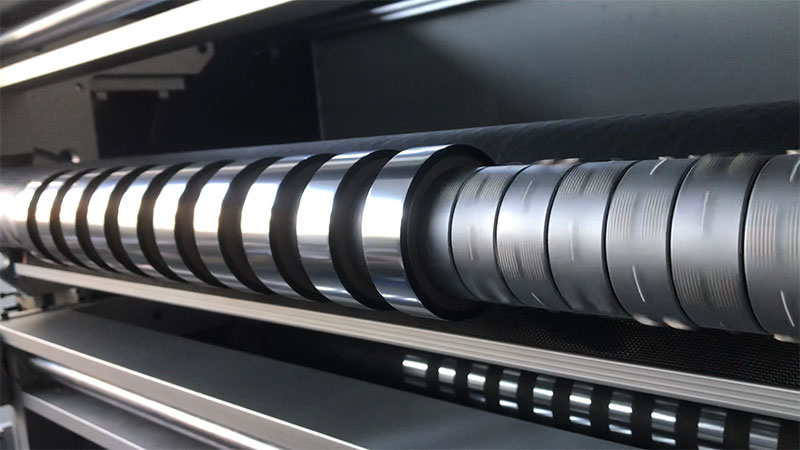

4. Process adaptability is enhanced
• Multi-material compatibility: The same machine can accurately cut different materials (such as metal foils, flexible circuit boards, fiber fabrics) to meet the needs of high-mix production.
• Complex shape cutting: Special-shaped cutting (e.g., curves, zigzag edges) can be achieved through dynamic cutter heads or rotating knives, expanding product design possibilities.
5. Automation & Process Control
• Real-time monitoring and adjustment: Integrated sensors (such as tension control, thickness detection) provide immediate feedback and correction of cutting parameters to avoid human error.
• Data traceability: record the cutting parameters of each batch, which is convenient for quality traceability and process optimization.
6. Quality assurance of downstream processes
• Reduce subsequent defects: For example, in the production of lithium batteries, the accuracy of the slitting of the pole piece directly affects the alignment of the winding and avoids the risk of short circuit; In the packaging industry, precise slitting ensures a tight seal.
• Improve terminal performance: For example, the slitting accuracy of optical film material affects the brightness and uniformity of display equipment.
Examples of application scenarios
• New energy field: lithium battery separator slitting accuracy ≤± 0.5μm to prevent dendrite puncture.
• Electronics industry: FPC (flexible circuit board) slitting edge without copper foil warping to ensure that the line is on.
• Medical materials: medical tape is cut without fiber shedding, which meets the requirements of sterility.
Technical support
• High rigidity mechanical structure: reduces cutting jitter caused by vibration.
• Closed-loop control system: such as linear motor drive + grating scale feedback, positioning accuracy up to micron level.
• Intelligent algorithms: AI predicts tool wear and automatically compensates for long-term stability.
Through the above technical means, the high-precision slitting machine not only improves the quality index of the product itself, but also reduces costs and enhances market competitiveness from the perspective of the overall production chain, especially in high value-added industries (such as semiconductors, new energy) It has become a key process link.

In the future, hot stamping foil slitting machines will continue to evolve towards deep intelligence and system integration.
06. February, 2026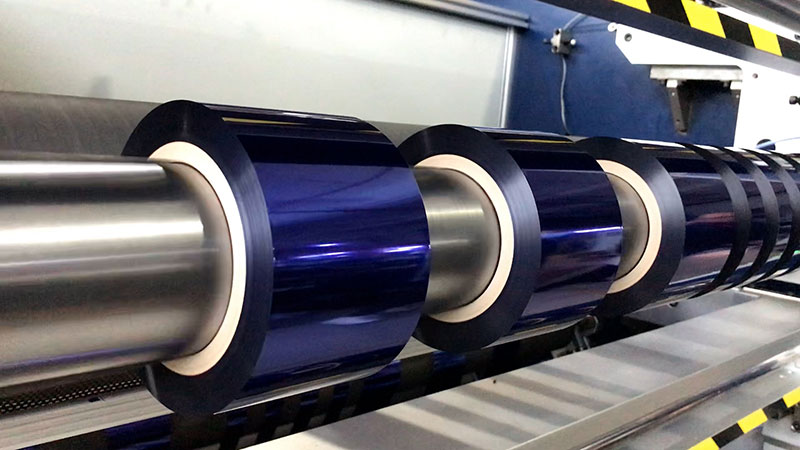
With the emergence of high-precision hot stamping foil slitting machines, this industry pain point is being fundamentally solved.
30. December, 2025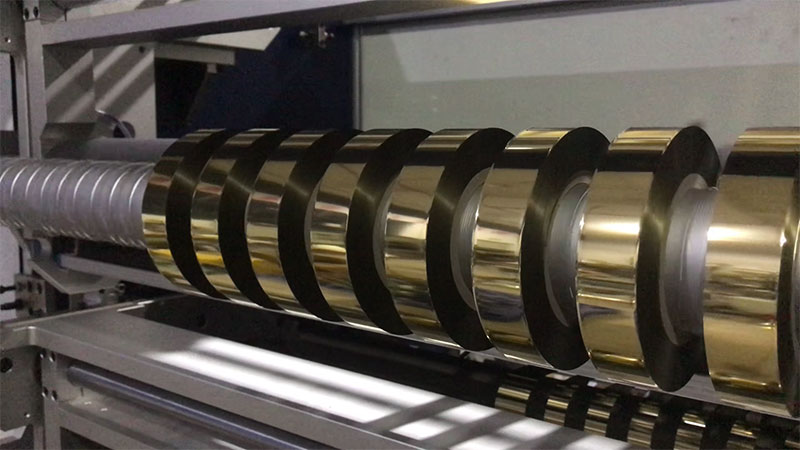
In the hot stamping process, the slitting quality of hot stamping foil is a key factor affecting the loss rate, production efficiency, and final product quality.
26. September, 2025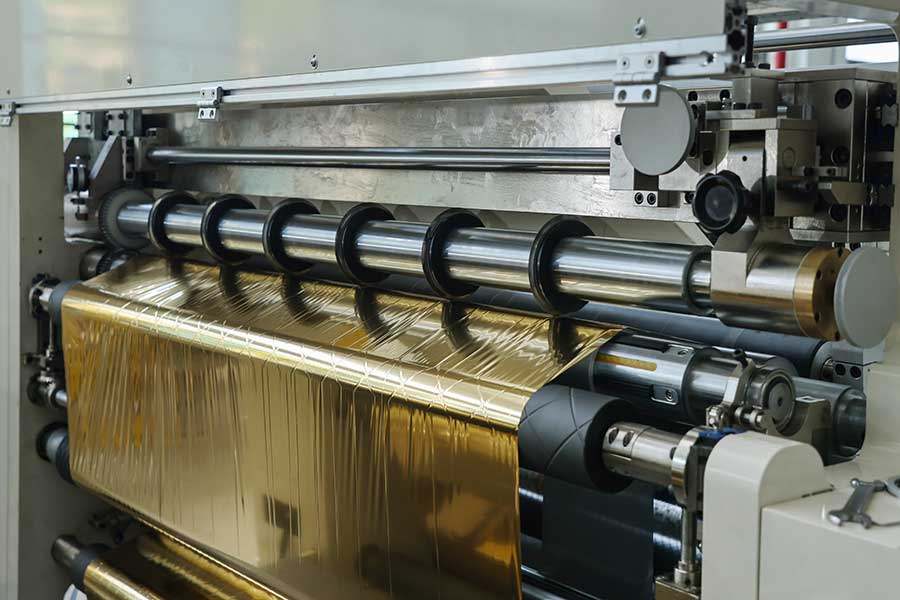
In today's highly expensive and competitive manufacturing environment, any bit of material waste can directly eat into profits.
25. September, 2025
High-precision slitting is not just a simple narrowing of large coils of material, but a precision technology that integrates mechanical engineering, materials science and process control
19. September, 2025