Slitter rewinders play a vital role in the label printing industry, and their core functions are to improve production efficiency, ensure product quality, and adapt to diverse customer needs. Here's a detailed breakdown of its key role and selection recommendations:
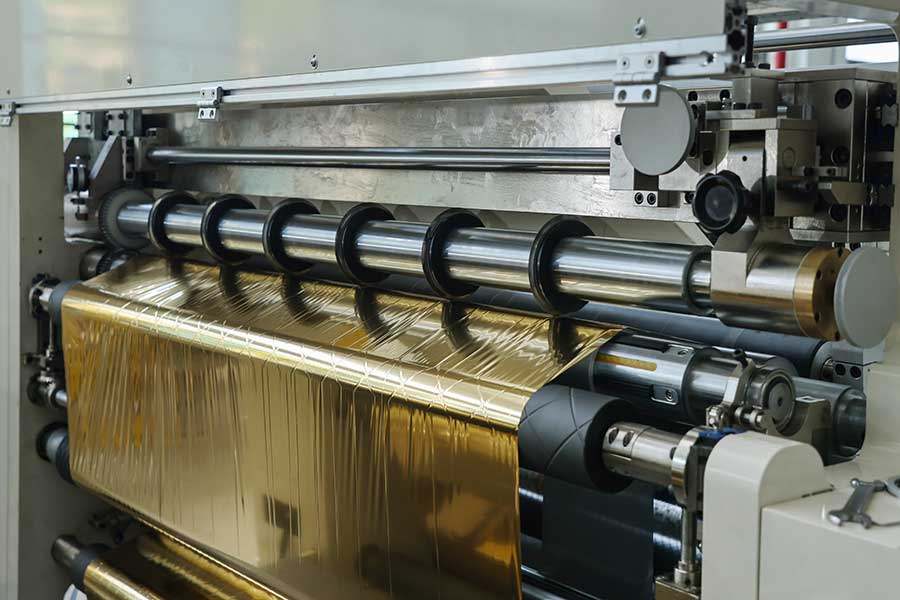

First, the key role of slitting and rewinding machine
1. Precision control
◦ Slitting accuracy: The slitting error of ±0.1mm is achieved through high-precision tool systems (such as pneumatic knives or servo-driven knives) to ensure that the edge of the label is smooth and burr-free, and the printed content is avoided from being cut.
◦ Tension control: Closed-loop tension systems (e.g., magnetic particle brakes or servo motors) are used to avoid tensile deformation of materials, especially for thin film (PE/PET) and tissue paper (e.g. self-adhesive) materials.
2. Efficiency improvement
◦ High-speed rewinding: modern equipment can reach 300-600 m/min, with automatic roll changing device (such as tower winding), reducing downtime and suitable for large volume orders.
◦ Simultaneous output of multiple rolls: Through the multi-axis slitting design, multiple small rolls (such as label rolls, in-mold label rolls) can be produced by slitting at one time, which can be directly connected to the subsequent die-cutting or labeling processes.
3. Material adaptability
◦ Handle a variety of substrates: such as coated paper, synthetic paper, dumb silver dragon, etc., need to be equipped with adjustable pressure rollers and static eliminators to prevent material delamination or static adsorption of dust.
◦ Special process support: Some models support in-line cold stamping and slitting after lamination to reduce the back-end process.
4. Waste disposal and environmental protection
◦ Integrated scrap recovery system (automatic winding or shredding) to reduce material waste, especially for high-cost materials such as RFID tag substrates.
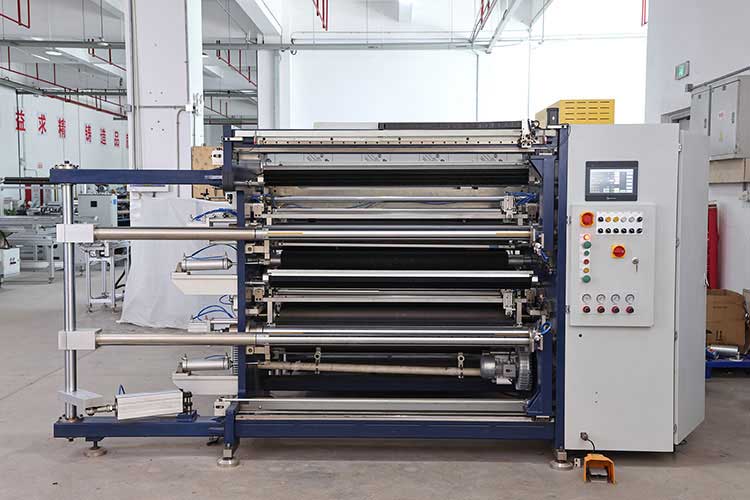

Second, the core considerations for selection
1. Material properties
◦ Thin/sensitive materials: Choose a model equipped with a low-pressure contact slitting knife and a precision tension zone to avoid wrinkles in the material (e.g., films below 40gsm).
◦ Thick/composite materials: require high rigidity tools and stronger tension control (e.g. for slitting multi-layer labels).
2. Production scale
◦ Small batches and high variety: Priority is given to quick-change systems (e.g., hydraulic quick-change tool holders) and preset parameter memory.
◦ Continuous production in large quantities: Choose a model with automatic inspection (e.g., CCD defect detection) and intelligent reel function.
3. Process requirements
◦ High-precision tags (e.g., electronic tags): The equipment is required to be equipped with a laser edge alignment system and a real-time deviation correction device (±0.05mm).
◦ Special shape slitting: For example, special-shaped labels need to be equipped with CNC toolpath adjustment function.
4. Intelligence and scalability
◦ Data interface: support MES/ERP system docking to achieve production data traceability (such as the number of cutting meters, defect location records).
◦ Future upgrades: Reserve the installation space for the die-cutting unit and inkjet device.
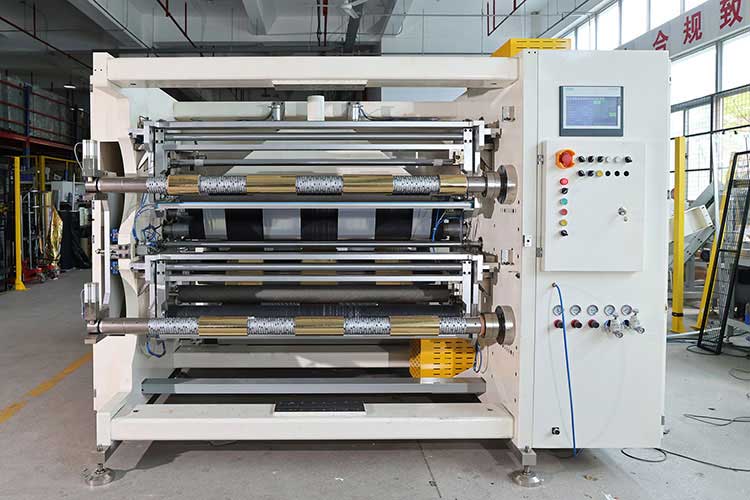

Third, recommended configuration scheme
| Application scenarios | Recommended |
| High-end electronic tags | Servo slitting + CCD detection + constant tension control, accuracy ± 0.05mm |
| Daily chemical self-adhesive labels | Pneumatic knife slitting + automatic waste discharge, speed ≥ 400m/min |
| In-mold labeling | Cold pressing slitting technology + anti-static system to avoid film deformation |
| Variable information labels | The in-line inkjet coding and slitting all-in-one machine supports dynamic slitting position adjustment |
Fourth, maintenance and cost optimization suggestions
• Tool maintenance: Regular maintenance with high-precision sharpeners to avoid slitting burrs.
• Energy consumption management: choose the variable frequency drive system to reduce standby energy consumption (for example, the energy saving mode of Aowei slitting machine can save 15% of electricity).
• Training points: Operators need to master the tension curve setting to match the material properties to avoid human error leading to roll scrap.
Fifth, industry trends
• Green slitting: The demand for solvent-free material slitting technology is rising, and the equipment needs to adapt to environmentally friendly substrates (such as degradable films).
• Intelligent: The AI slitting path optimization system is gradually popular, and the material utilization rate can be improved by 3%-5% through historical data learning.
Through precise selection, the slitting and rewinding machine can become the core equipment for label printing enterprises to enhance their competitiveness, especially in the market environment of personalized customization and short-run business growth, its role will be further highlighted.

This is not only an iteration of equipment, but also a comprehensive redefinition of production efficiency, material utilization and intelligent management standards.
27. February, 2026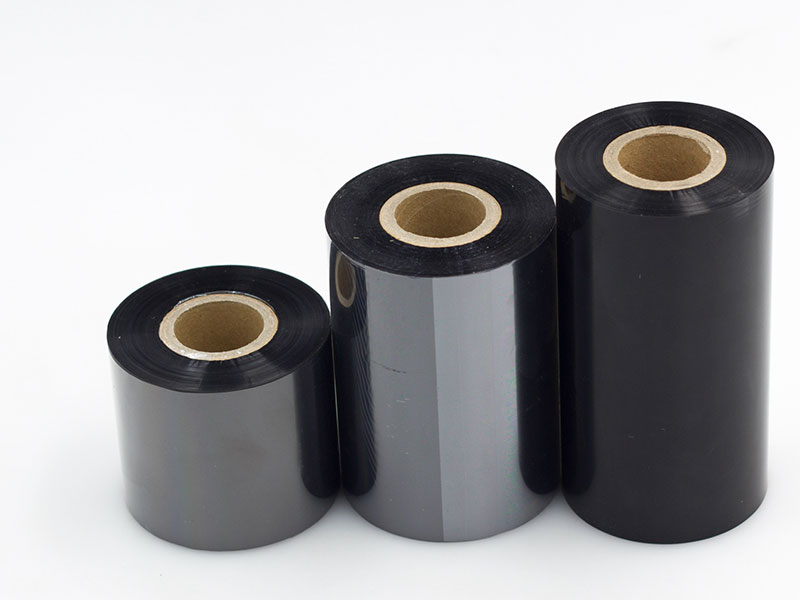
It is in this context that the new generation of ribbon slitting machines is redefining the production standards of the industry with "precision manufacturing" as the core.
27. February, 2026
this once management pain point is now transforming into a powerful tool for printing enterprises to reduce costs and increase efficiency.
26. February, 2026
This article will delve into how to make the hot foil slitting machine the engine of your production process optimization through scientific equipment selection and management.
26. February, 2026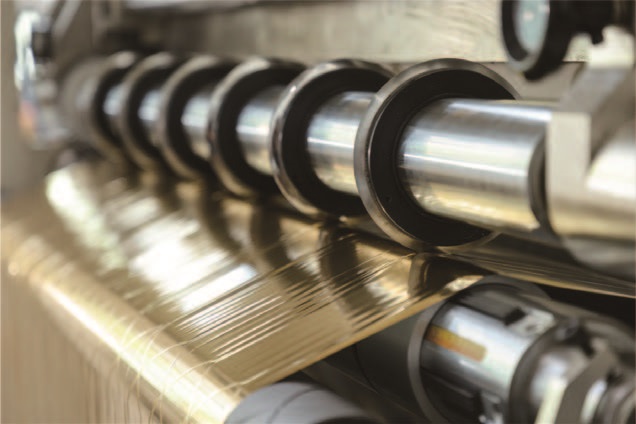
A precision platform that integrates multifunctional applications with cross-disciplinary process expansion.
26. February, 2026