summary
In the hot stamping process, the slitting quality of hot stamping foil is a key factor affecting the loss rate, production efficiency, and final product quality. The traditional post-inspection or passive adjustment mode is no longer able to meet the demand for high-quality, low-cost production. This scheme introduces the concept of "reliability design", systematically analyzes the root causes of slitting defects, and constructs a forward-looking and preventive control system from the four dimensions of equipment, materials, processes and management, aiming to fundamentally minimize slitting defects and achieve accurate, controllable and continuous reduction of hot stamping foil loss.
1. Problem definition: types and effects of slitting defects
Slitting defects mainly refer to various quality problems in the process of hot stamping foil in the winding process, which directly leads to the unusable or defective products in the hot stamping process.
• 1.1 Common types of slitting defects:
◦ Burr/serrated edge: The edge of the foil belt is not smooth due to the lack of sharpness or lack of precision of the cutting knife, and it is easy to produce flying gold and tailing during hot stamping.
◦ Uneven end face (chrysanthemum pattern): Uneven winding tension or equipment vibration leads to uneven end face of foil coil, which affects the stability of unwinding and is very easy to cause foil breakage.
◦ Longitudinal stripes (dark lines): There are small gaps or foreign objects on the slitting knife, leaving scratches or indentations on the foil surface, and the pattern is missing or abnormal after hot stamping.
◦ Cutting/drawing: Excessive cutter pressure or poor toughness of the base film can cause the foil to be completely cut off or partially involved in the drawing.
◦ Tight edge: The tension on both sides is inconsistent during slitting, resulting in loosening of the foil roll while tightening, and deviation and wrinkle during unwinding.
• 1.2 Direct consequences:
◦ Soaring loss rate: Defective parts must be eliminated, directly increasing the cost of raw materials.
◦ Reduced production efficiency: Frequent shutdowns to deal with problems such as foil breakage and deviation, reducing equipment utilization.
◦ Quality risk: Minor defects may flow into the subsequent process, resulting in batch hot stamping defective products.
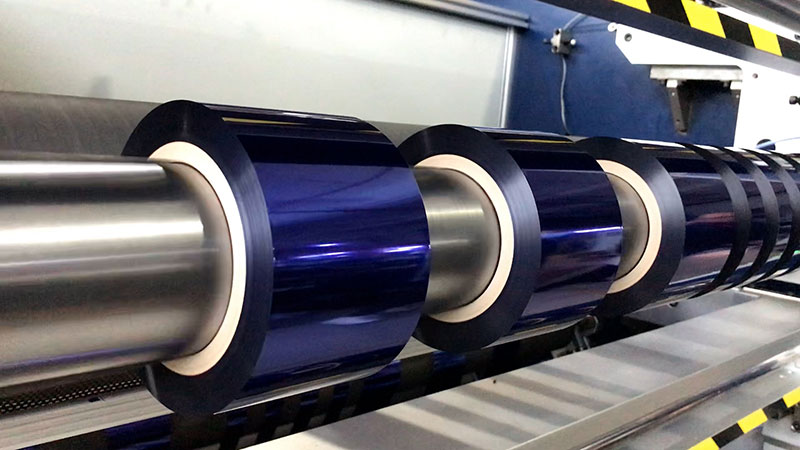

2. Core concept: reliability design from "post-remediation" to "pre-prevention"
The core of reliability design is to eliminate potential failure modes through systematic design and control in the early stages of product or process development, ensuring stable and reliable operation throughout its life cycle.
Applied to hot foil slitting means that we cannot only inspect and eliminate defective products after the slitting is completed, but must create a stable system that is "not prone to slitting defects".
3. Four-dimensional control scheme based on reliability design
This scheme constructs a control system from four interrelated dimensions to ensure the inherent reliability of the slitting process.
Dimension 1: Reliability design of equipment and tools
This is the physical basis for achieving high-quality slitting.
1. High-precision slitting machine selection and maintenance:
◦ Design selection: Preferential selection of slitting machines with high rigidity frames, precision servo drives, and tension closed-loop control systems (within ± 0.5%) is preferred to reduce vibration and tension fluctuations from the source.
◦ Preventive maintenance system: Establish a strict regular maintenance schedule, including bearing lubrication, transmission component inspection, and calibration of the correction system, to ensure that the equipment is always in optimal condition.
2. Reliability Management of Cutter Systems:
◦ Tool material and coating: Choose a special alloy steel or ceramic insert based on the characteristics of the hot stamping foil (e.g., PET base film, coating hardness), and apply a wear-resistant coating (e.g., DLC) to extend the life.
◦ Edge angle and grinding: Standardize the cutting edge angle (such as 30°) and entrust professional manufacturers to perform high-precision grinding to ensure sharp edges and no microscopic notches.
◦ Clamping accuracy control: Standardize the mounting of the blade using a torque wrench, ensuring that the blade clearance and overlap are precisely adjustable and stable.
Dimension 2: Reliability design of material handling
The state of the hot stamping foil itself is an intrinsic variable that affects the quality of the slitting.
1. Incoming Inspection and Storage Standardization:
◦ Establish access standards: put forward clear requirements for the supplier's master coil end face neatness, core roundness, and film surface tension uniformity.
◦ Standardized storage: Control the temperature and humidity of the warehouse (e.g., 23±2°C, 55%±5%RH) to prevent moisture or physical deformation of the foil.
2. Pre-processing before boarding:
◦ Environmental balance: Before production, the hot stamping foil master roll is left in the workshop for a sufficient time to balance it with the temperature and humidity of the production environment to reduce internal stress.
◦ Surface Cleaning: Use a dust-free cloth and ion gun to gently clean the surface of the master coil to remove tiny particles that could damage the blade.
Dimension 3: Reliability design of process parameters
Determine the optimal process window through scientific experiments and achieve precise control.
1. Parameter DOE Optimization:
◦ Experimental design: For different materials and widths of hot stamping foil, the interaction of key parameters such as slitting speed, unwinding/unwinding tension, blade pressure, and taper control is systematically studied through experimental design methods.
◦ Establish a parameter library: After determining the optimal parameter combination, standardize it and enter it into the database to form a "slitting recipe" for different products.
2. Process monitoring and closed-loop feedback:
◦ Online monitoring: CCD visual inspection system is installed to monitor the quality of the slitting edge and the neatness of the end face in real time, and immediately alarm if abnormalities are found.
◦ Real-time tension control: Using high-precision sensors to feedback tension data in real time, the system automatically fine-tunes to ensure constant tension.
Dimension 4: Reliability design of personnel and management
Ensure that the above measures are implemented correctly and consistently.
1. Standardized Operating Procedures:
◦ Formulate SOP: Prepare detailed slitting operation instructions, covering the whole process from picking, knife loading, parameter setting, first article inspection to process inspection, so as to achieve "rules to follow".
2. Full staff training and qualification certification:
◦ System training: not only training the operation skills, but also the operator to understand the slitting principle, the cause of defects and the concept of reliability.
◦ Certification: Operators are assessed and certified to ensure that they have the ability to execute SOPs and handle basic exceptions.
3. Continuous Improvement Mechanism:
◦ Establish a loss database: Record in detail the slitting loss rate, defect type, and cause of each coil.
◦ Regular review: Regularly hold quality analysis meetings to use data-driven decision-making to continuously optimize process parameters and management processes.
4. Program implementation and expected benefits
1. Implementation Path:
◦ Phase 1 (Diagnosis and Planning): Assess existing equipment, processes, and management levels to identify weak links.
◦ Phase 2 (Infrastructure): Establish equipment maintenance system, SOP framework and parameter database.
◦ Phase 3 (Pilot and Optimization): Select typical product lines for pilot, verify the effectiveness of the scheme, and continuously optimize it.
◦ The fourth stage (comprehensive promotion and solidification): promote it throughout the company and solidify the successful experience into an enterprise standard.
2. Expected benefits:
◦ Direct economic benefits: The loss rate of hot stamping foil is expected to be reduced by 30% - 50%.
◦ Improved efficiency: Reduced downtime due to slitting issues and improved overall equipment efficiency.
◦ Quality improvement: The through-through rate of the hot stamping process has been significantly improved, and the customer complaint rate has decreased.
◦ Management upgrade: form a data-based and standardized refined management model to improve the team's professional ability.
conclusion
Say goodbye to slitting defects, which can not be achieved by relying on the improvement of a single link. The foil loss control system proposed in this scheme is based on reliability design, and by building a "four-in-one" preventive ecosystem covering equipment, materials, processes and management, the threshold of quality control is moved forward, and the post-inspection is shifted to pre-prevention and in-process control. This can not only effectively reduce losses and save costs, but also significantly improve the stability of the production process and the market competitiveness of products, laying a solid foundation for the sustainable development of enterprises.

The leap in its core competitiveness stems from the comprehensive empowerment of intelligent control technology.
11. February, 2026
This article will delve into the design innovations and technological breakthroughs of modern hot stamping foil slitting machines in achieving high stability and durability.
11. February, 2026
a sophisticated system that combines mechanical engineering, materials science, and intelligent control.
11. February, 2026
hot stamping foil slitting machine, which is silently promoting the precision and efficiency of the entire industry as an "expert in customized slitting solutions".
09. February, 2026
the new generation of hot stamping foil slitting machine is moving towards the goal of "zero waste and precise slitting" through a series of innovative technologies.
09. February, 2026