To ensure the long life and low maintenance cost of the hot stamping foil slitting machine, it is necessary to comprehensively optimize from multiple links such as material selection, design, process, use and maintenance. Here's what to do:
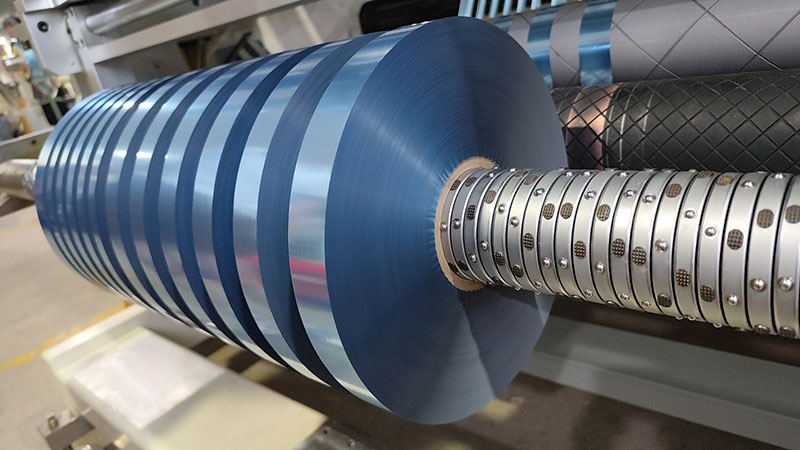
1. Material selection optimization: high-standard selection of key components
• Core cutting components (e.g. blades, spindles)
◦ Use high-hardness, high-wear-resistant materials (such as cemented carbide, ceramic coating or powder metallurgy steel) to ensure long-term cutting accuracy.
◦ The surface of the blade is treated with titanium plating (TiN, DLC, etc.) to reduce the adhesion and wear of hot stamping foil materials.
• Transmission systems (guides, bearings, gears)
◦ High-strength alloy steel or hardened steel with a self-lubricating coating (e.g., PTFE) to reduce frictional losses.
◦ Sealed maintenance-free bearings (e.g. SKF or NSK brands) are preferred.
• Airframe structure
◦ Use highly rigid materials such as cast iron or welded steel structures to avoid deformation caused by long-term vibration.
2. Process & Manufacturing: Precision Machining & Assembly
• Machining accuracy control
◦ The machining tolerance of key components (such as cutter shaft and guide rail) is controlled within ±0.005mm to ensure smooth operation.
◦ Dynamic balance test: Dynamic balance correction is required for high-speed rotating parts to reduce vibration and noise.
• Surface treatment
◦ Spray or electrophoretic coating of corrosive parts (e.g., frames) to improve environmental resistance.
◦ The sliding parts are mirror polished or laser hardened to reduce the coefficient of friction.
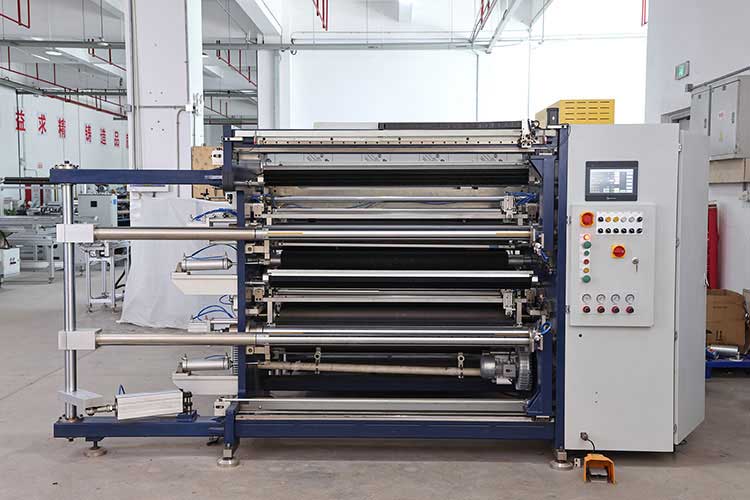

3. Design optimization: modularity and maintainability
• Modular design
◦ Separate cutting module, tension control module, etc., for quick replacement or maintenance.
• Quick replacement of wearing parts
◦ Blades, guide wheels, etc. are designed as quick-release structures to reduce downtime.
• Intelligent monitoring system
◦ Integrated vibration sensor and temperature sensor to monitor the equipment status in real time and warn of faults in advance (such as abnormal bearing heating).
4. Use and maintenance: standardize operation and preventive maintenance
• Code of Practice
◦ Avoid overload operation and calibrate the tension system regularly (too tight or too loose hot stamping foil will accelerate wear).
◦ Keep the environment clean and prevent the build-up of metal dust or hot stamping foil chips.
• Regular maintenance schedules
◦ Daily: Clean the blades and rails, check the pneumatic/hydraulic system pressure.
◦ Monthly: Lubricate transmission parts (using high-temperature grease) and check electrical wiring.
◦ Quarterly: Replace worn blades and verify system accuracy.
• Lubrication management
◦ Reduce manual intervention with centralized lubrication systems or long-life greases such as lithium greases.
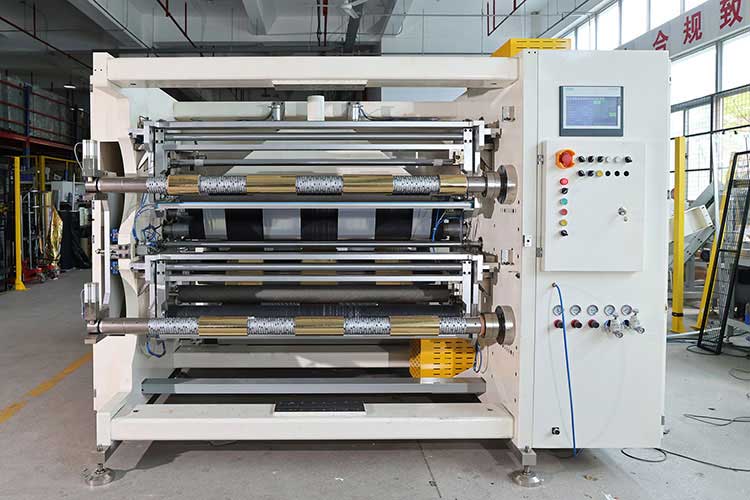

5. Energy-saving and consumption-reducing design
• Efficient drive system
◦ Servo motor + inverter control is selected to reduce energy waste and mechanical loss.
• Scrap recycling units
◦ Integrate waste collection system to reduce the frequency of cleaning and maintenance.
6. Suppliers and Technical Support
• Choose equipment suppliers with mature experience (such as Guowang, Omet, etc.) to ensure after-sales technical support.
• Maintain inventory of critical spare parts (e.g. blades, sensors) and shorten service intervals.
summary
Through the combination strategy of high-standard material selection + precision technology + intelligent design + standardized maintenance, the service life of the hot stamping foil slitting machine can be significantly improved (up to more than 10 years), and the maintenance cost can be reduced by 30%~50%. The focus is on preventive maintenance and early fault intervention, rather than after-the-fact repairs.
this once management pain point is now transforming into a powerful tool for printing enterprises to reduce costs and increase efficiency.
26. February, 2026
This article will delve into how to make the hot foil slitting machine the engine of your production process optimization through scientific equipment selection and management.
26. February, 2026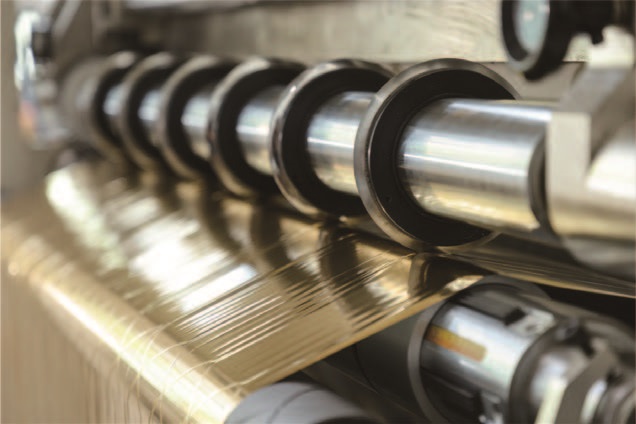
A precision platform that integrates multifunctional applications with cross-disciplinary process expansion.
26. February, 2026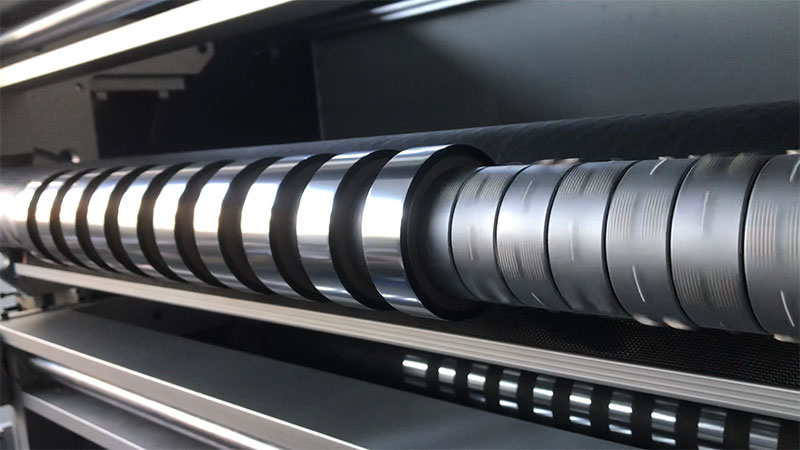
The leap in its core competitiveness stems from the comprehensive empowerment of intelligent control technology.
11. February, 2026
This article will delve into the design innovations and technological breakthroughs of modern hot stamping foil slitting machines in achieving high stability and durability.
11. February, 2026