When adjusting the parameters of the hot stamping foil slitting machine to adapt to different materials, it is necessary to comprehensively consider the material characteristics, slitting accuracy, machine performance and other factors. Here are the key steps and considerations:
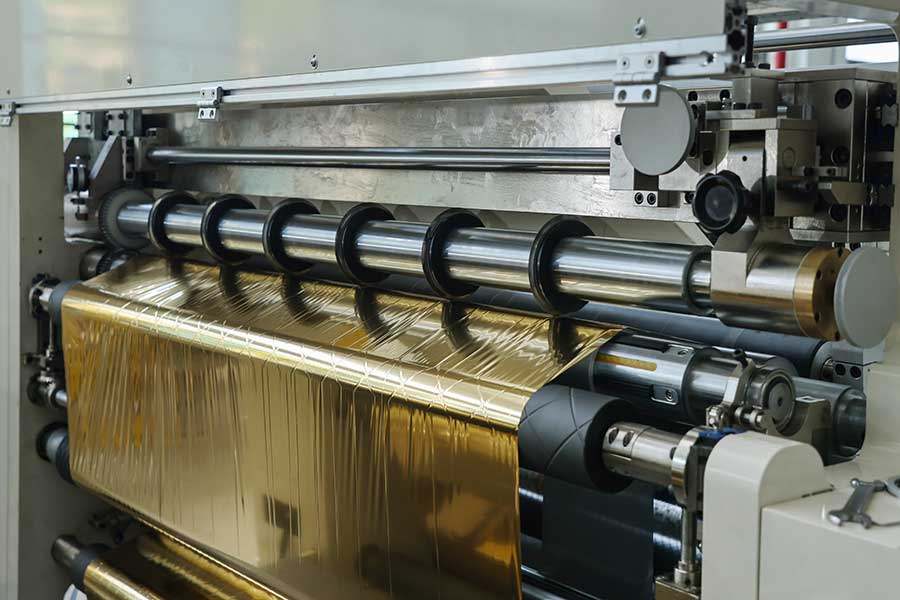

1. Clarify the material characteristics
• Material type: distinguish between substrates such as PET, OPP, PVC, and paper, as well as the thickness and hardness of the hot stamping layer.
• Heat sensitivity: Some materials are sensitive to temperature, and high temperatures may cause deformation or sticking.
• Tensile strength: Soft materials (such as thin PET) need to control tension to avoid tensile deformation.
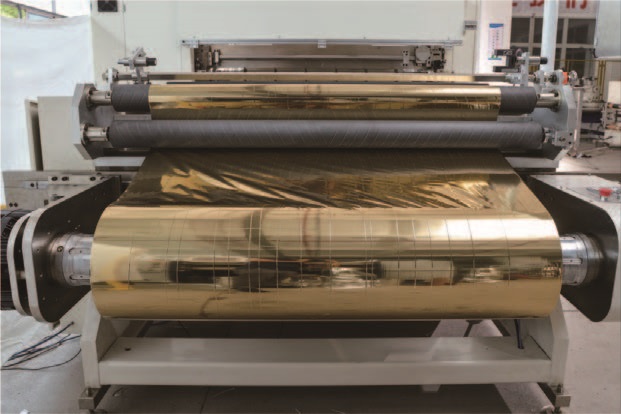

2. Adjust key parameters
(1) Slitting speed
• High hardness materials (e.g. thick PVC): reduce the speed (e.g. 30-50 m/min) to avoid edge wear or burrs.
• Soft materials (e.g. thin OPP): can be increased appropriately (e.g. 60-80 m/min), but with tension control.
(2) Tension control
• High tension materials (e.g. metal foil): High tension (e.g. 15-20N) is required to ensure smooth slitting.
• Low-tension materials (e.g. films): reduce tension (e.g. 5-10N) to prevent tensile deformation.
• Recommendation: Use a tension sensor for real-time monitoring and gradually fine-tune the material to be jitter-free and wrinkle-free.
(3) Tool selection and adjustment
• Blade type: Carbide knives are suitable for thick materials, and round blades are suitable for high-speed slitting of films.
• Tool angle: Adjust the inclination angle of the blade (usually 15°-30°) to reduce cutting resistance.
• Pitch pressure: Thick materials need to increase the pressure, thin materials need to be lightly pressed (to avoid indentation).
(4) Temperature control (if heating and slitting is required)
• High temperature materials (e.g. some composite foils): 80-120°C.
• Low temperature sensitive material: Turn off the heat or set the low temperature (≤50°C).
(5) Rewinding and unwinding parameters
• Winding tension: generally 80%-90% of the slitting tension, too large will cause core deformation.
• Winding ratio: large winding diameter (such as Φ300mm or more) needs to reduce the winding speed.
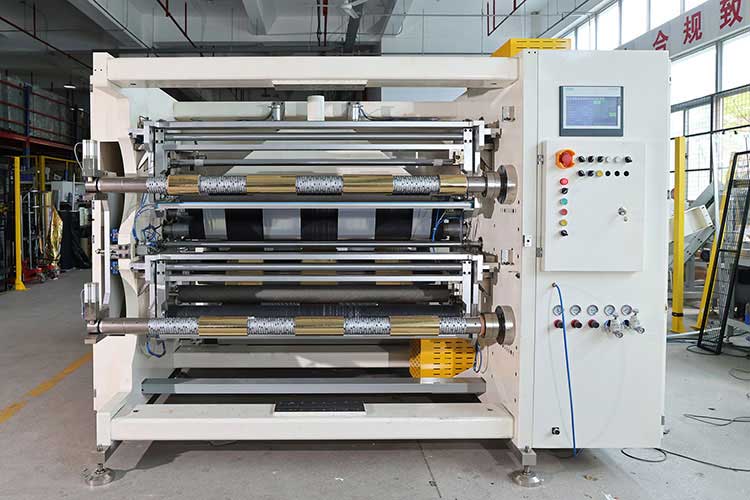

3. Test & Optimize
1. Sample test: first use scrap to test cut to see whether the slitting edge is smooth, whether there are burrs or delamination.
2. Parameter recording: record the best parameters of each material (such as speed, tension, knife pressure) and establish a database.
3. Dynamic adjustment: real-time monitoring of slitting quality in production, timely fine-tuning of parameters.
4. FAQ Resolution
• Flash/burr: Check blade sharpness or increase tension.
• Material wrinkling: reduce tension or adjust guide roller parallelism.
• Web eccentricity: Check whether the winding shaft is level and adjust the guiding system.
5. Equipment maintenance
• Clean the knives and guide rollers regularly to avoid dust accumulation affecting the slitting accuracy.
• Lubricate the transmission parts to ensure the stability of the tension system.
Through systematic adjustment and continuous optimization, the slitting efficiency and quality can be significantly improved. Different brands of equipment may vary, it is recommended to refer to the equipment manual and adjust it based on actual experience.
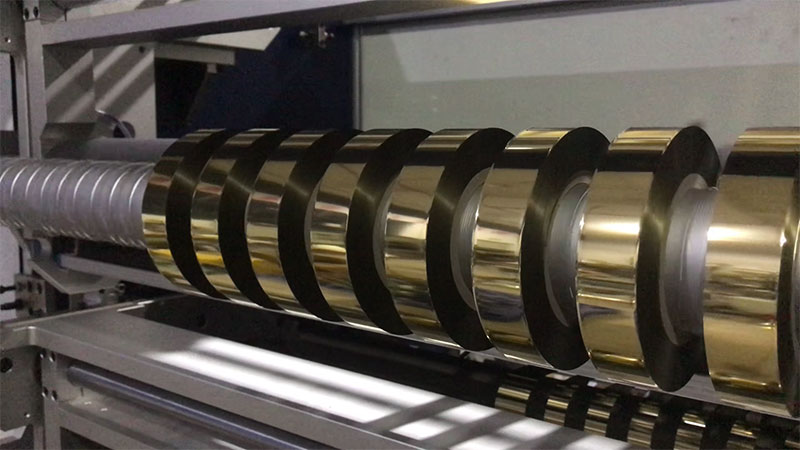
this once management pain point is now transforming into a powerful tool for printing enterprises to reduce costs and increase efficiency.
26. February, 2026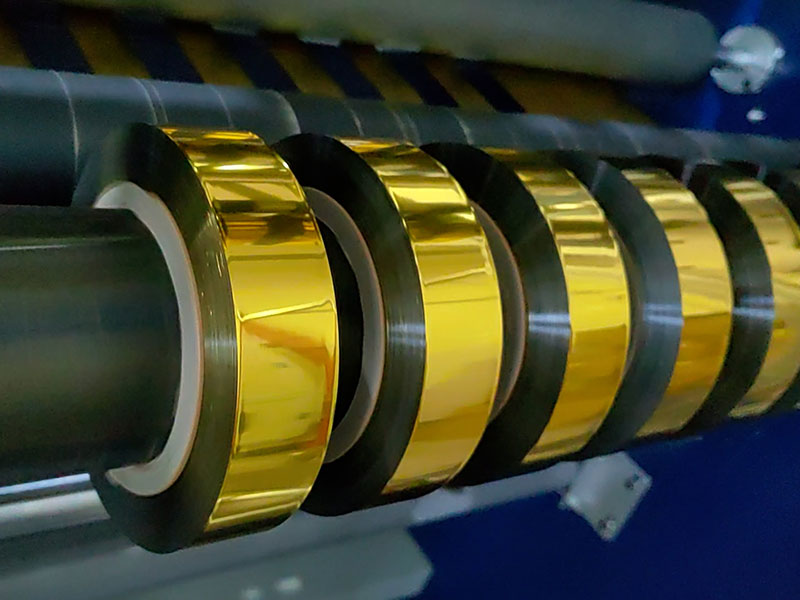
This article will delve into how to make the hot foil slitting machine the engine of your production process optimization through scientific equipment selection and management.
26. February, 2026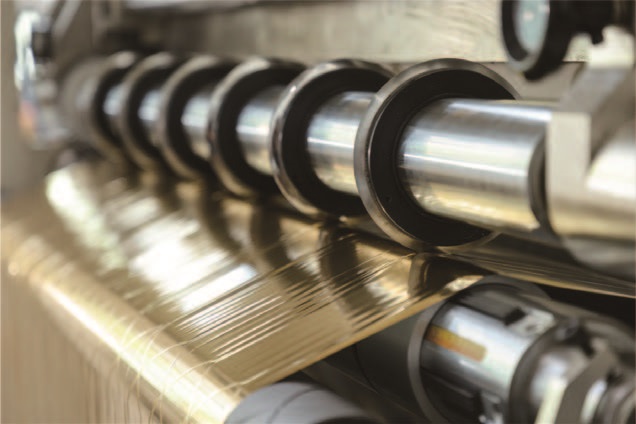
A precision platform that integrates multifunctional applications with cross-disciplinary process expansion.
26. February, 2026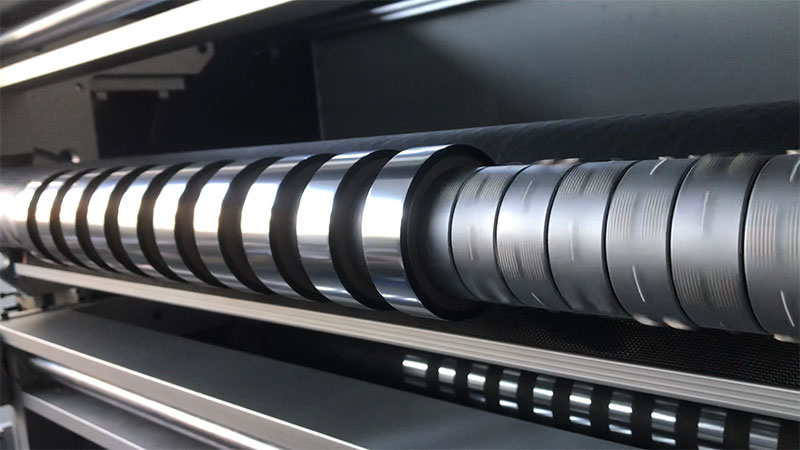
The leap in its core competitiveness stems from the comprehensive empowerment of intelligent control technology.
11. February, 2026
This article will delve into the design innovations and technological breakthroughs of modern hot stamping foil slitting machines in achieving high stability and durability.
11. February, 2026