As a key equipment in modern manufacturing, the multi-functional application of slitting machine from rough machining to fine cutting has significantly improved the efficiency and precision of material processing. Here's a systematic breakdown of its multi-functional applications:
First, the basic working principle of the slitting machine
The slitting machine uses cutting media such as blades, lasers, or high-pressure water jets to cut coils (such as metals, films, paper, composite materials, etc.) longitudinally according to a preset width or shape. The core process includes unwinding→ web guiding → cutting → winding, and the control system adjusts the tension, speed and cutting accuracy.
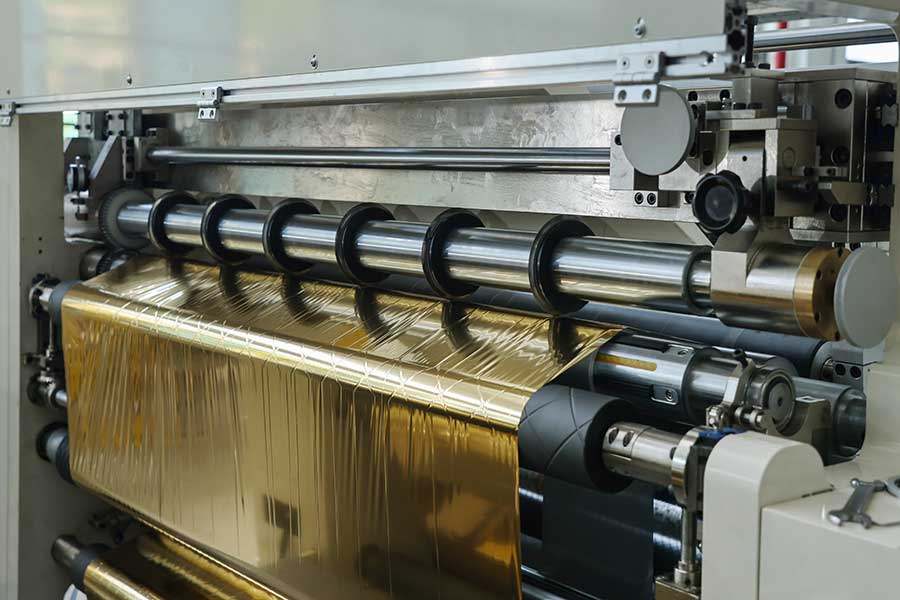

Second, the advanced application from rough machining to fine cutting
1. Roughing stage: efficient slitting
• Application scenario: Preliminary slitting or edge removal of materials, with low precision requirements (more than ±1mm) and focus on efficiency.
• Technical features:
◦ Use a high-strength round knife or shear knife to adapt to thick plates (e.g., steel plate, rubber plate).
◦ High speed operation (100-300 m/min), suitable for mass production.
◦ Case: Preliminary slitting of metal coils, which is convenient for subsequent deep processing.
2. Semi-finishing stage: standardized slitting
• Application scenarios: Medium accuracy (±0.1mm-±0.5mm), such as PCB substrates and packaging films in the electronics industry.
• Technical features:
◦ Servo control system is used to adjust the tension to reduce the tensile deformation of the material.
◦ Equipped with in-line detection (e.g., CCD camera) to monitor edge quality in real time.
◦ Case: Lithium battery pole piece slitting to ensure width consistency.
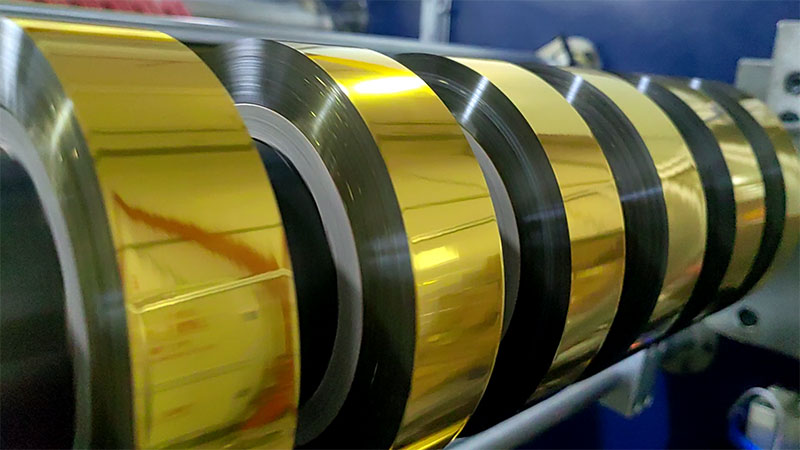

3. Fine cutting stage: high-precision machining
• Application scenarios: micron-level accuracy (within ±0.01mm), such as optical film and ultra-thin copper foil.
• Technical features:
◦ Use laser slitting or air-suspended round knives to avoid mechanical stress on the material.
◦ Constant temperature environment control to reduce thermal deformation.
◦ Case: Slitting of flexible substrate for OLED display, no burrs at the edges.
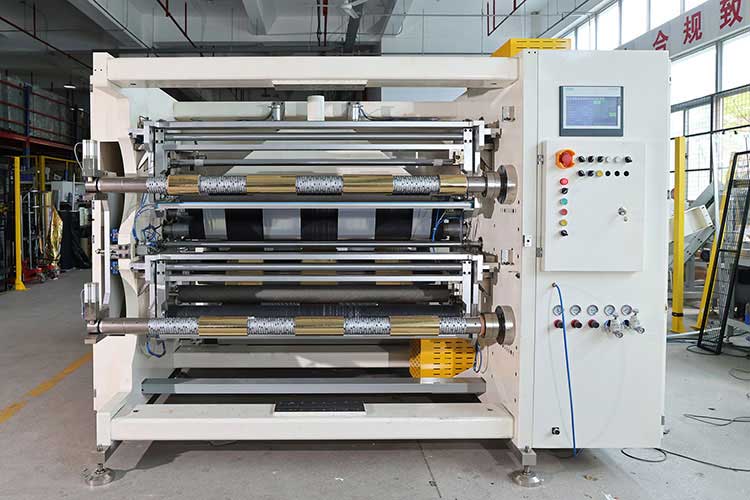
Third, multi-functional expansion application of slitting machine
1. Compound slitting
◦ Simultaneous completion of slitting and composite processes (such as film + aluminum foil) for the processing of barrier layers in food packaging.
2. Special-shaped cutting
◦ Non-straight cutting of curves and wavy shapes by numerical control system (CNC) is suitable for automotive interiors or medical materials.
3. Intelligent upgrade
◦ Integrated AI algorithm predicts blade wear and automatically adjusts cutting parameters; The Internet of Things (IoT) enables remote monitoring.

Fourth, industry application cases
• New energy field:
Power battery separator slitting requires a dust-free environment, with an accuracy of ±2μm, and the use of static elimination and ultrasonic cutting technology.
• Packaging industry:
High-speed slitting of BOPP film (600 m/min) with automatic tool change system to reduce downtime.
Fifth, technical challenges and future trends
• Challenges: Tension control of ultra-thin materials (e.g. ≤5 μm), tool life of highly hardness materials (carbon fiber).
•Trend:
◦ Green manufacturing: Low energy consumption design, reduce material waste.
◦ Modular slitting machine: quickly switch between different process requirements.
epilogue
The technological evolution of slitting machines is driving the manufacturing industry towards high-precision and flexible production. The multi-functional integration from roughing to fine cutting not only improves efficiency, but also expands the boundaries of its application in high-end fields. In the future, with the development of intelligence and new materials, slitting technology will further break through the physical limits.
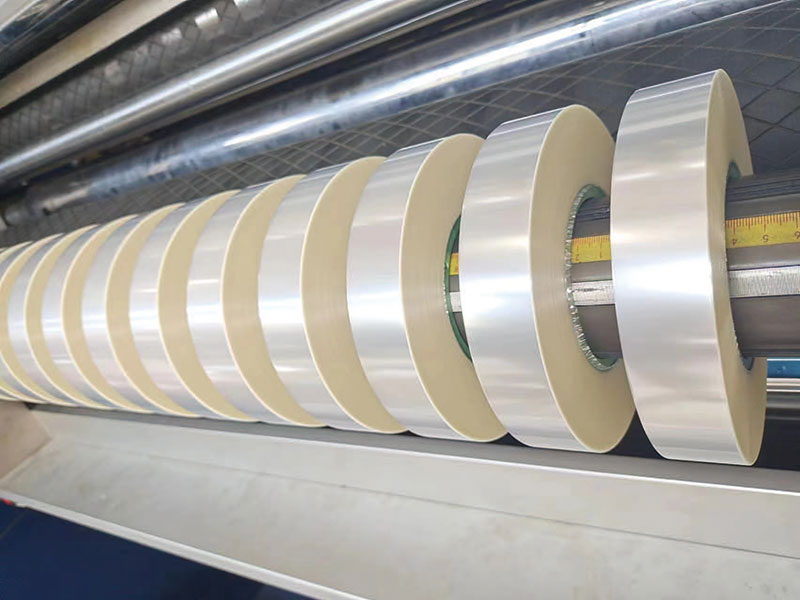

It is not just a simple "cutting", but a precision process of tension control, face neatness and winding quality.
27. February, 2026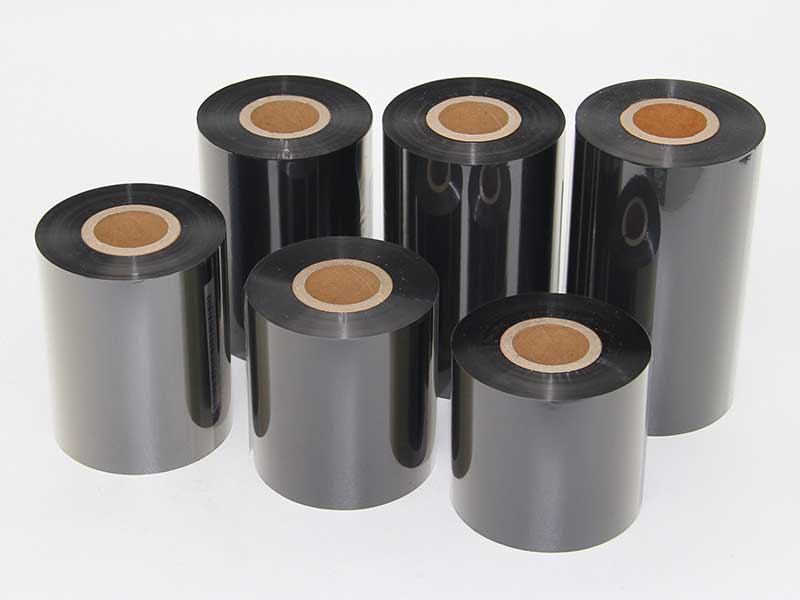
This is not only an iteration of equipment, but also a comprehensive redefinition of production efficiency, material utilization and intelligent management standards.
27. February, 2026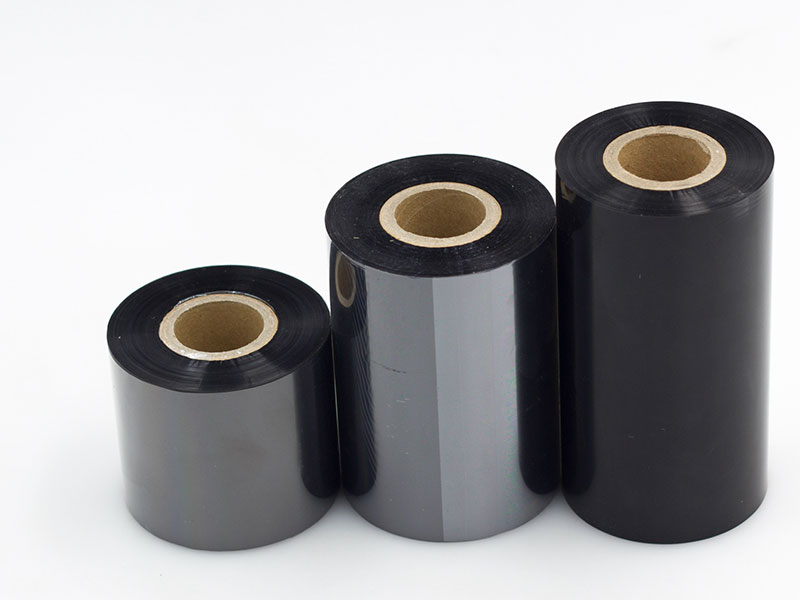
It is in this context that the new generation of ribbon slitting machines is redefining the production standards of the industry with "precision manufacturing" as the core.
27. February, 2026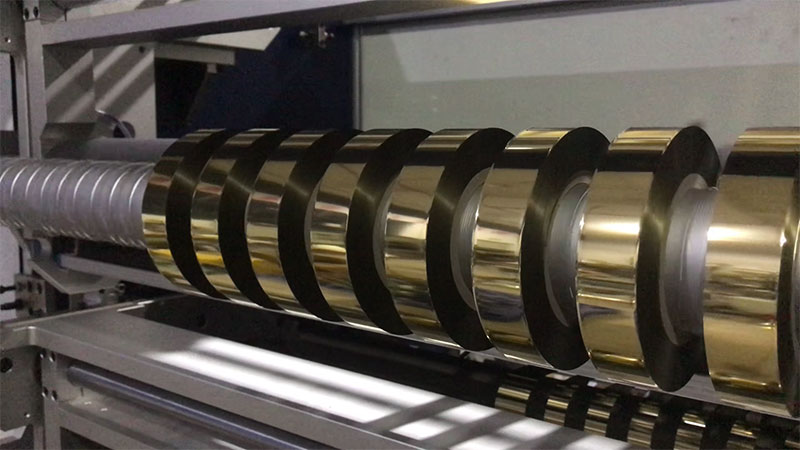
this once management pain point is now transforming into a powerful tool for printing enterprises to reduce costs and increase efficiency.
26. February, 2026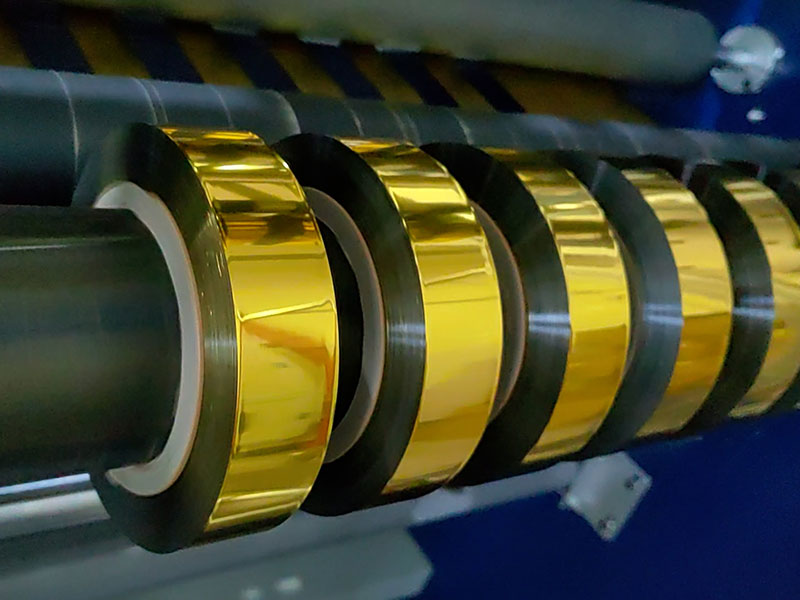
This article will delve into how to make the hot foil slitting machine the engine of your production process optimization through scientific equipment selection and management.
26. February, 2026